How Computers Talk, Stay Safe, and Grow Smarter
A simple guide to networks, the cloud, AI, and modern systems
Let’s start with an easy picture.
Imagine a town where many buildings need to talk to each other. Some buildings are hospitals. Some are schools. Some are offices. Some are homes.
To talk and share things, they need roads. In the computer world, those roads are called networks.
This post explains, in clear and simple words, how modern computer networks are designed so they:
Keep working without stopping
Stay safe from danger
Grow without breaking
Become smarter using AI and automation
This is written for complete beginners. If you are new to computer science, this is for you.
What Is a Computer Network?
A computer network is how computers:
Send messages
Share files
Run applications
Help people work and communicate
Today, networks power almost everything:
Healthcare systems
Mobile phones
Cloud applications
Robots and automation
Artificial intelligence tools
When a network fails:
Applications stop working
Important information can be lost
People lose trust
That is why network design matters so much.
The Three Big Goals of Every Network
1. Safety
Safety means protecting systems and data.
A safe network:
Checks who you are before letting you in
Protects information so strangers cannot read it
Watches activity all the time
Think of it like a secured building:
You must show an ID
Doors are locked
Security watches the entrance
This is especially important in healthcare, where patient data must stay private.
2. Reliability
Reliability means the network keeps working even when something goes wrong.
A reliable network:
Has backup paths
Can recover quickly from failures
Avoids single points of failure
It is like having:
Backup electricity
Extra water supply
Emergency plans
3. Growth
Growth means the network can expand without needing to be rebuilt.
A growing network:
Supports more users
Handles more applications
Adapts to new technology
Think of building with blocks. You can add more blocks without tearing down what you already built.
Simple Rules for Modern Network Design
Trust Is Always Verified
Modern networks do not trust users just because they are “inside.”
They verify:
Who you are
What device you are using
What you are trying to access
This idea is called Zero Trust.
Every request must prove it is allowed. This greatly reduces security risks.
Build Systems in Small Pieces
Instead of one large system, networks are built in smaller parts:
Security components
Connectivity components
Monitoring components
This makes systems easier to:
Fix
Upgrade
Scale
Watch the Network at All Times
Modern networks are always observed. They collect:
Performance numbers
System messages
Activity paths
Watching these signals helps teams detect problems early and fix them before users notice.
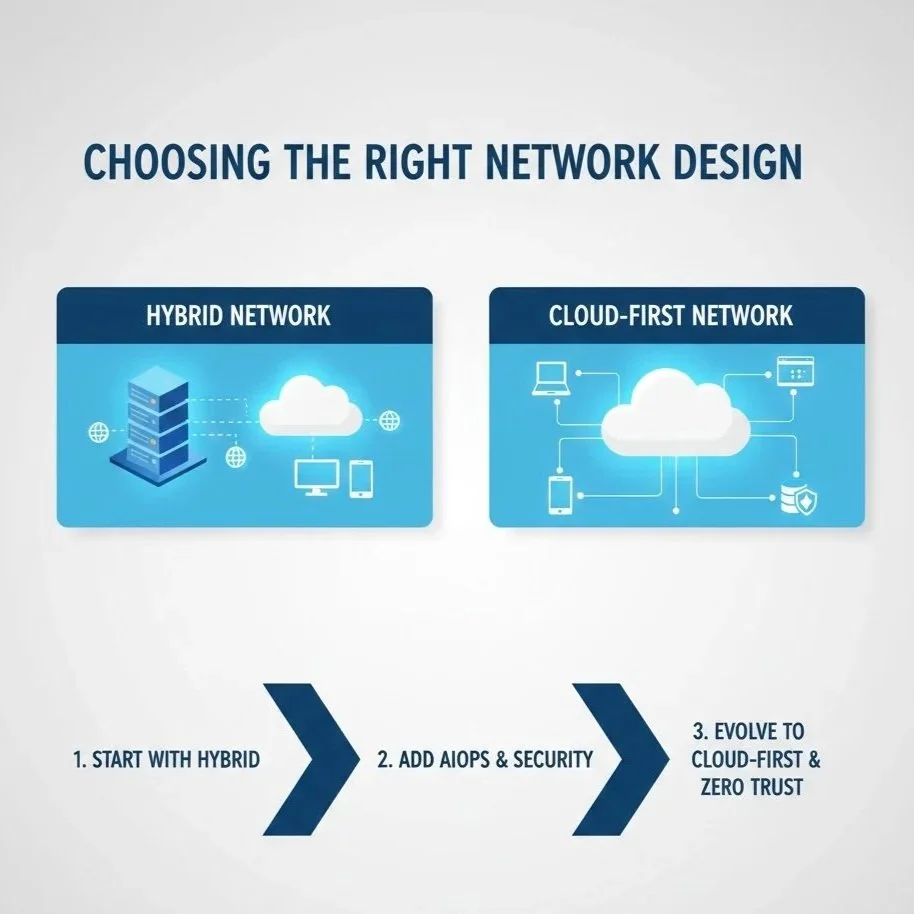
Network Design Option 1: Hybrid Network with SD-WAN
This design works well for organizations that:
Already have offices or data centers
Are slowly moving to the cloud
It combines:
On-site systems
Cloud systems
Smart routing over the internet
SD-WAN chooses the best path for data based on speed and quality.
If one path fails, traffic moves automatically to another path. This improves uptime and supports steady growth.
Network Design Option 2: Cloud-First with Zero Trust
This design fits organizations that:
Use many cloud applications
Support remote or hybrid workers
Operate across multiple locations
Instead of routing everyone through one central office:
Users connect to nearby cloud security points
Security rules are applied immediately
Access depends on identity, not location
This approach is:
Highly secure
Easy to scale
Well suited for modern work environments
Making Networks Smarter with AI and Automation
Modern networks do not rely only on humans.
They use:
Artificial intelligence to detect unusual behavior
Machine learning to learn patterns over time
Automation to respond to problems quickly
Examples include:
Automatically rerouting traffic when performance drops
Blocking devices that show risky behavior
Grouping many alerts into one clear problem
This approach is called AIOps, or AI for IT operations. It helps systems react faster and reduces downtime.
Choosing the Right Design
Both network designs are useful.
Hybrid networks are good for gradual cloud adoption
Cloud-first designs are ideal for distributed and modern systems
Many organizations:
Start with a hybrid model
Add strong monitoring and automation
Move toward Zero Trust and cloud-first designs over time
This reduces risk while preparing for the future.
Why This Matters for Healthcare
In healthcare:
Systems must always be available
Data must be protected
Failures can affect patient care
AI-powered, cloud-based networks help:
Predict failures before they happen
Reduce system downtime
Protect sensitive medical data
Allow healthcare workers to focus on patients
This is where computer science directly supports human well-being.
Key Idea to Remember
A good network is safe, reliable, and able to grow.
When combined with AI and automation, it becomes smart enough to protect and heal itself.
Learning Resources for Beginners
If you want to learn more, start with these beginner-friendly topics and tools:
Basic Concepts
What is a computer network
What the cloud is and how it works
How the internet moves data
Cloud Foundations
Introduction to cloud services (compute, storage, networking)
Cloud-native design basics
High availability and scalability
Security Basics
Identity and access control
Zero Trust security concepts
Data protection and encryption
AI and Automation
What artificial intelligence is
How machine learning learns from data
How automation reduces human effort
Hands-On Learning
Simple cloud labs using free tiers
Network diagrams and simulations
Basic monitoring dashboards
These foundations prepare you to understand advanced topics like AIOps, robotics, and self-healing systems.
Part of My Ph.D. Learning Journey
This post is part of a continuing blog series following my Ph.D. journey in Computer Science, with a focus on:
Artificial intelligence
Machine learning
Robotics and automation
Cloud-native systems
Healthcare system reliability
The goal of this series is simple:
to explain complex technology in clear language and use it to build safer, smarter healthcare systems for the future.